


Finance
Author: Cashflow-Brasil - Created: 04/30/2025 - 04:45 PM - Reviewed: 06/01/2025 - 04:45 PM
Financial education is one of the most important pillars for the development of a financially healthy and conscious society. When this learning starts in childhood, the benefits are even greater. Teaching children how to handle money responsibly prepares future adults to face financial challenges and make more conscious decisions.
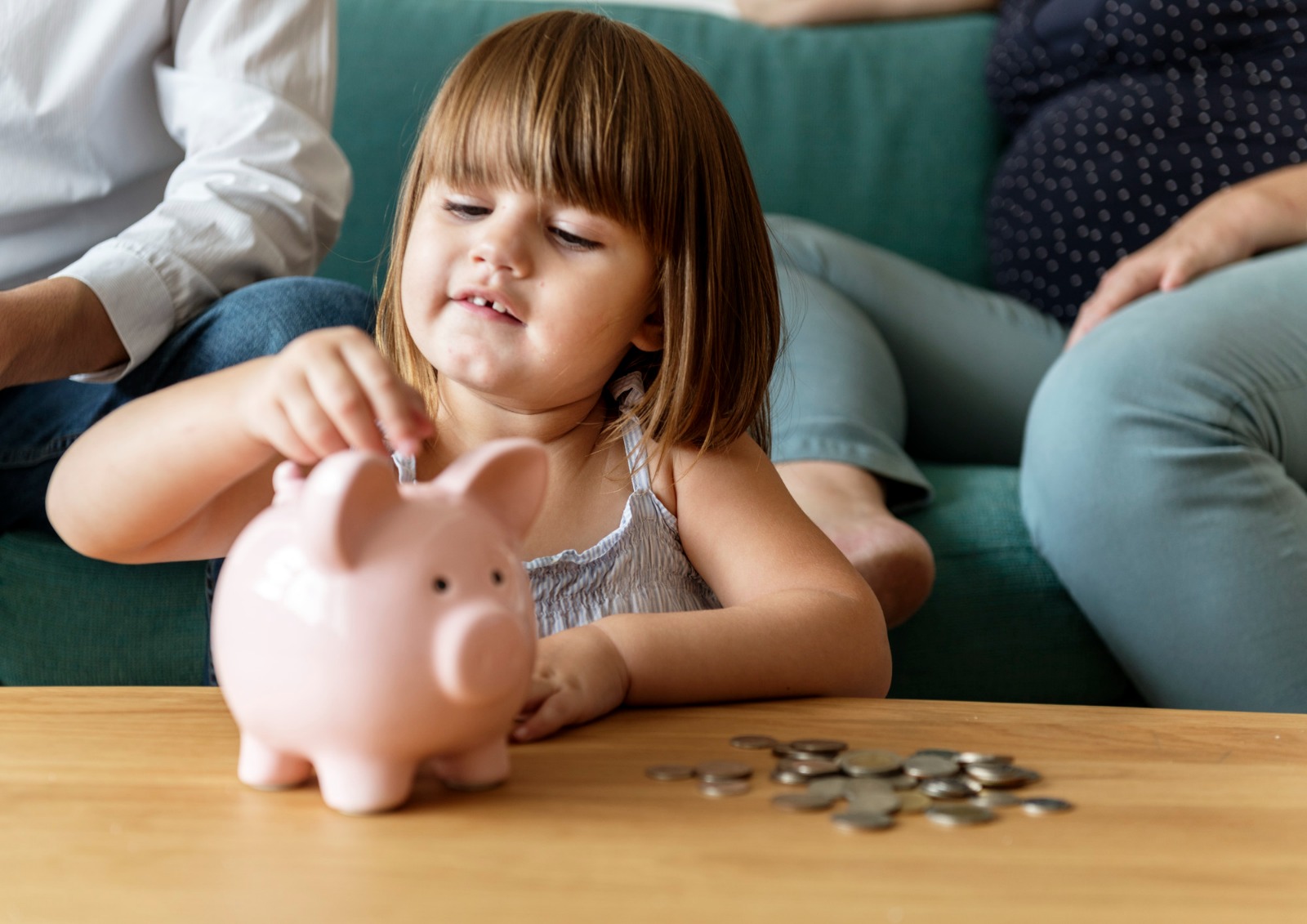

In childhood, the brain is in full development and has a great capacity to absorb new concepts. By teaching basic concepts such as saving, planning, and conscious spending early on, we are building a solid foundation for future financial behavior. Just as we teach brushing teeth or respecting others, financial education should be part of children's daily learning routine.
It doesn't have to be complicated. Children can learn in a playful and practical way. Here are some examples of topics that can be introduced early:
Today, there are many materials available to help parents and educators in this mission. Children's books about money, board games focused on finance, educational apps, and animated videos are some examples. The important thing is to adapt the language and medium to the child's age so that learning happens naturally and in a fun way.
Books like "The Money Boy", Who Moved My Cheese, and others aimed at children's reality help connect the concepts to their real-world environment, using characters they can relate to.
Games like "Monopoly" or child-friendly resource management versions teach about risk, investment, and planning in a fun and interactive way.
With the advancement of technology, many children's finance apps allow simulating saving, earnings, and goals. Additionally, YouTube channels with simple explanations can complement formal education.
Schools play an essential role in this process, but they cannot replace the influence of the family. When parents and educators work together, the child internalizes financial values and habits much more effectively. It is important for adults to also seek to improve their own financial education to serve as examples.
Teaching financial education from childhood is an investment in the future. Children who learn to handle money healthily become more conscious, prepared adults, less prone to debt and impulsive decisions. The earlier this learning begins, the better the results will be throughout life. It is up to us, adults, to provide the resources, examples, and guidance to ensure this new generation grows with a strong and balanced financial mindset.